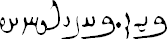Afrikaans|Afrikaans Living
What is it?
Afrikaans is a Low Franconian West Germanic language descended from Dutch and spoken mainly in South Africa and Namibia. There are also speakers of Afrikaans in Australia, Belgium, Botswana, Canada, Germany, Lesotho, Malawi, Namibia, the Netherlands, New Zealand, the UK, the USA, Zambia and Zimbabwe. About 7.2 million people speak Afrikaans as a native language, and a further 8-15 million speak it as a second language.
Afrikaans retains some features of 18th century Dutch, together with vocabulary from various Bantu and Khoisan languages and also from Portugese and Malay. Speakers of Afrikaans can understand Dutch, though Dutch speakers tend to need a while to tune into Afrikaans.
From about 1815 Afrikaans started to replace Malay as the language of instruction in Muslim schools in South Africa. At that time it was written with the Arabic alphabet. Afrikaans, written with the Latin alphabet, started to appeared in newspapers and political and religious works in about 1850. Then in 1875 a group of Afrikaans speakers from the Cape formed the Genootskap vir Regte Afrikaanders (Society for Real Afrikaners), and published a number of books in Afrikaans, including grammars, dictionaries, religious material and histories. They also published a journal called the Patriot.
During the early years of the 20th century there was a blossoming of academic interest in Afrikaans. In 1925 Afrikaans was recognised by the government as a real language, instead of a slang version of Dutch. Afrikaans has changed little since then.
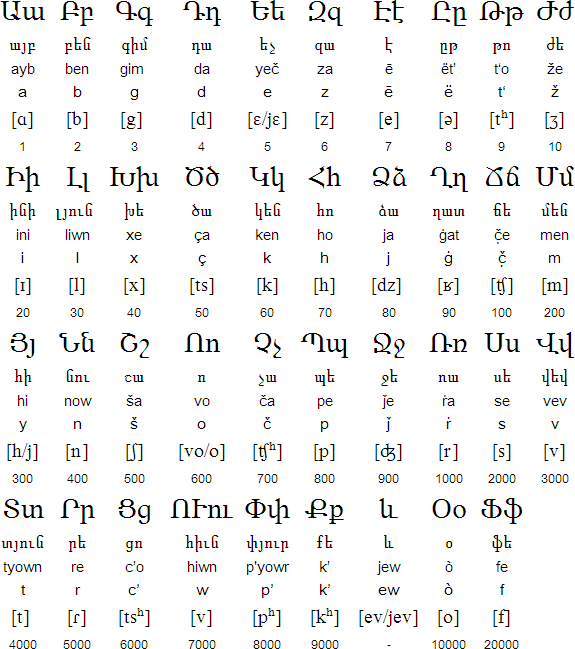
Alphabet:
| A a | B b | C c | D d | E e | F f | G g | H h | I i |
|---|
| aa | bee | see | dee | ee | ef | gee | haa | ie |
| J j | K k | L l | M m | N n | O o | P p | Q q | R r |
|---|
| jee | kaa | el | em | en | oo | pee | kuu | er |
| S s | T t | U u | V v | W w | X x | Y y | Z z | |
|---|
| es | tee | uu | vee | wee | ex | y | set |
Sample Text:
Alle menslike wesens word vry, met gelyke waardigheid en regte, gebore. Hulle het rede en gewete en behoort in die gees van broederskap teenoor mekaar op te tree.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
Greetings:
Hallo! Hallo!
Hoe gaan dit? How are you?
Goeie more! Good morning!
Goeie dag! Good day!
Goeie naand! Good evening!
Goeie nag! Good night!
Goeie bye! Good bye!
Tips: www.easyafrikaans.com/easyafrikaans/Basic_Grammar.html
www.exploresouthafrica.net/phrasebook.htm
Source: www.omniglot.com